A Journey from Chaos to Excellence
In the high-stakes world of modern manufacturing, where a single defective component can ground an aircraft or recall thousands of vehicles, there exists a guardian process that stands between potential disaster and engineering excellence. This guardian is the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP), and its story is one of transformation, innovation, and the relentless pursuit of quality that has reshaped entire industries.
Imagine, for a moment, the automotive industry of the 1980s. Suppliers operated in relative isolation, manufacturing parts based on drawings and specifications, but with little systematic verification that their processes could consistently deliver the required quality. Quality issues were discovered late in the process, often after parts had already been shipped to customers, resulting in costly recalls and damaged reputations. It was against this backdrop of quality uncertainty that the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) developed PPAP—a revolutionary approach that would fundamentally change how industries ensure quality and reliability.
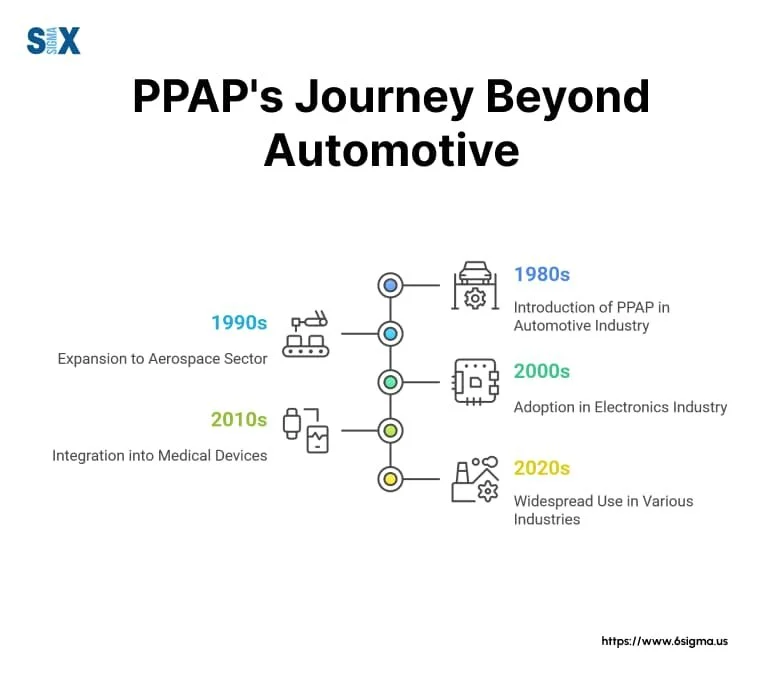
PPAP’s Journey Beyond Automotive: From automotive to aerospace, electronics, and medical devices, PPAP has seen widespread use across various industries.
The Genesis of a Quality Revolution
The story of PPAP begins with a simple yet profound realisation: prevention is infinitely more valuable than correction. In the traditional manufacturing paradigm, quality was often an afterthought—something to be inspected rather than built into the process. The cost of poor quality in manufacturing typically ranges from 15-40% of revenue, representing an enormous opportunity for improvement.
PPAP emerged as a standardised methodology that fundamentally shifted the quality paradigm from reactive to proactive. Rather than discovering problems after production, PPAP requires suppliers to demonstrate their capability before mass production begins. This seemingly simple shift has generated remarkable results: companies implementing robust quality management systems, including PPAP, have seen an average return of $6 in revenue for every $1 invested.
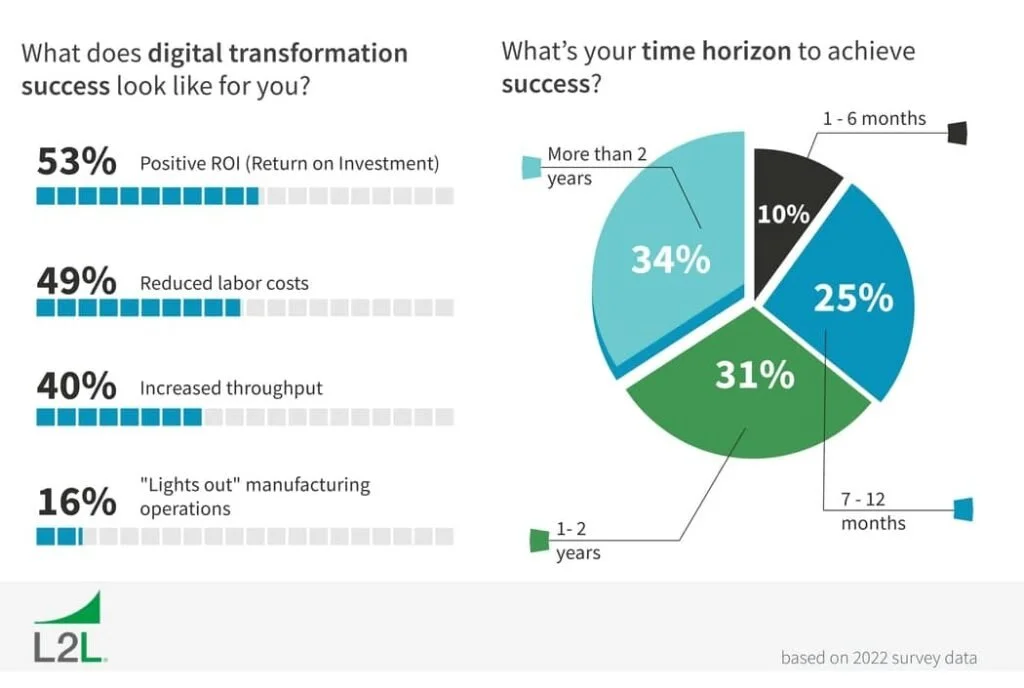
Survey Results On The Outcomes And Time Horizon For Digital Transformation Success
The Evolution of Excellence: From Manual to AI-Enhanced
The journey of PPAP implementation has been one of continuous evolution, marked by dramatic improvements in both efficiency and accuracy. Traditional manual PPAP processes once required up to 96 hours of labour per submission, with accuracy scores hovering around 6.0 on a 10-point scale. Today, AI-enhanced PPAP systems can complete the same process in just one hour with accuracy scores exceeding 9.8.
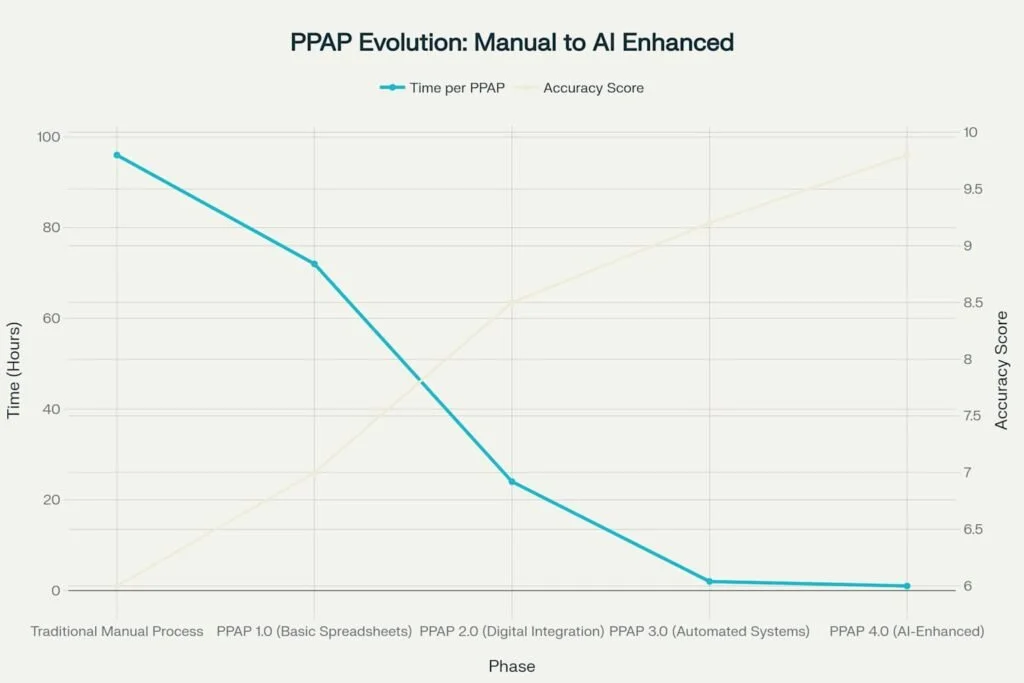
PPAP Implementation Evolution: Transformation from Manual Processes to AI-Enhanced Systems
This transformation didn’t happen overnight. It represents decades of technological advancement and process refinement. The evolution from PPAP 1.0 (basic spreadsheets) to PPAP 4.0 (AI-enhanced systems) has delivered efficiency gains of up to 4,200%, fundamentally changing how engineering firms approach quality documentation.
The Eighteen Pillars of Quality: Understanding PPAP Elements
At the heart of PPAP lies a comprehensive framework of 18 elements, each serving as a critical pillar in the architecture of quality assurance. These elements range from design records and engineering change documentation to dimensional results and part submission warrants. However, not all elements carry equal weight for every organisation—particularly for engineering design and drafting service providers like KEVOS.

PPAP Elements Analysis: Relationship between Quality Impact and Implementation Complexity
The relationship between quality impact and implementation complexity varies significantly across the 18 PPAP elements. For engineering firms, elements such as Design Records, Engineering Change Documents, and Dimensional Results represent critical, high-impact areas that directly align with their core competencies. These elements not only deliver the highest quality improvements but also provide the greatest opportunity for engineering firms to differentiate themselves in the marketplace.
Real-World Transformation: The J&L Manufacturing Success Story
To understand the true power of PPAP implementation, consider the remarkable transformation of J&L Manufacturing, an ISO 9001 certified job shop specialising in complex CNC machining and metal fabrication. Christy Wiggam, the company’s quality manager, faced a daunting challenge: PPAP submissions that consumed an entire week of effort, creating a significant bottleneck that limited the company’s ability to accept new business.
The traditional process was painfully manual. Christy would take paper copies of customer prints, mark each dimension with yellow stickers, scan drawings into her computer, and manually type each dimension into Excel templates. The creation of Process FMEAs, control plans, and process flows followed the same laborious pattern. This approach not only consumed precious time but also introduced opportunities for human error.
The transformation came through digital integration and process automation. By implementing modern PPAP management software, J&L Manufacturing achieved a remarkable outcome: Christy now completes over 168 PPAPs annually—more than one per day on average. This represents a productivity improvement that seemed impossible under the old manual system.

Several colourful gears are arranged to interlock, symbolising teamwork and interconnectedness
The Financial Reality: PPAP’s Return on Investment
The financial benefits of PPAP implementation extend far beyond time savings. Research consistently demonstrates that quality management initiatives, including PPAP, generate substantial returns across multiple dimensions. Companies implementing comprehensive quality programs see an average of $16 in cost reduction for every dollar invested.
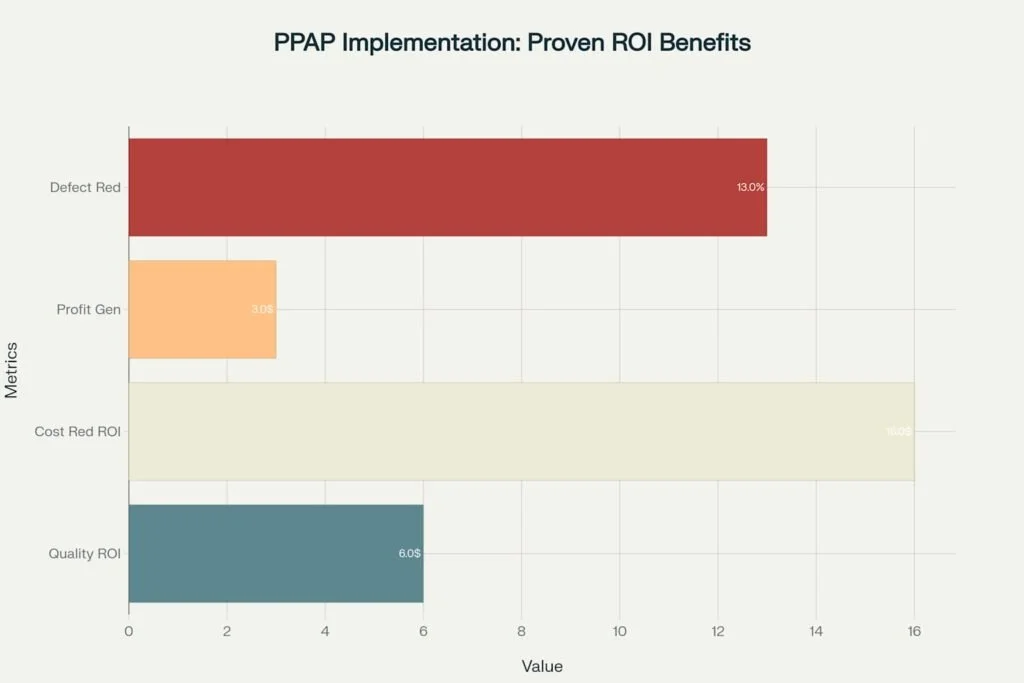
PPAP ROI Metrics: Demonstrating the Financial and Quality Benefits of Implementation
The specific benefits of PPAP implementation are particularly compelling for the automotive and aerospace industries. Supplier defect rates can be reduced by as much as 13%, while process time improvements can reach extraordinary levels—in some cases exceeding 4,000% efficiency gains. These improvements translate directly to bottom-line benefits: reduced warranty costs, fewer recalls, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced competitive positioning.
Digital Transformation: The Modern PPAP Landscape
Today’s manufacturing environment is characterised by rapid digital transformation, with companies at various stages of their quality digitisation journey. Current research indicates that 42% of manufacturers are in the initial progress stage of digital transformation, while only a small percentage have achieved fully digital factory status. This presents both a challenge and an opportunity for engineering firms seeking to leverage PPAP for competitive advantage.
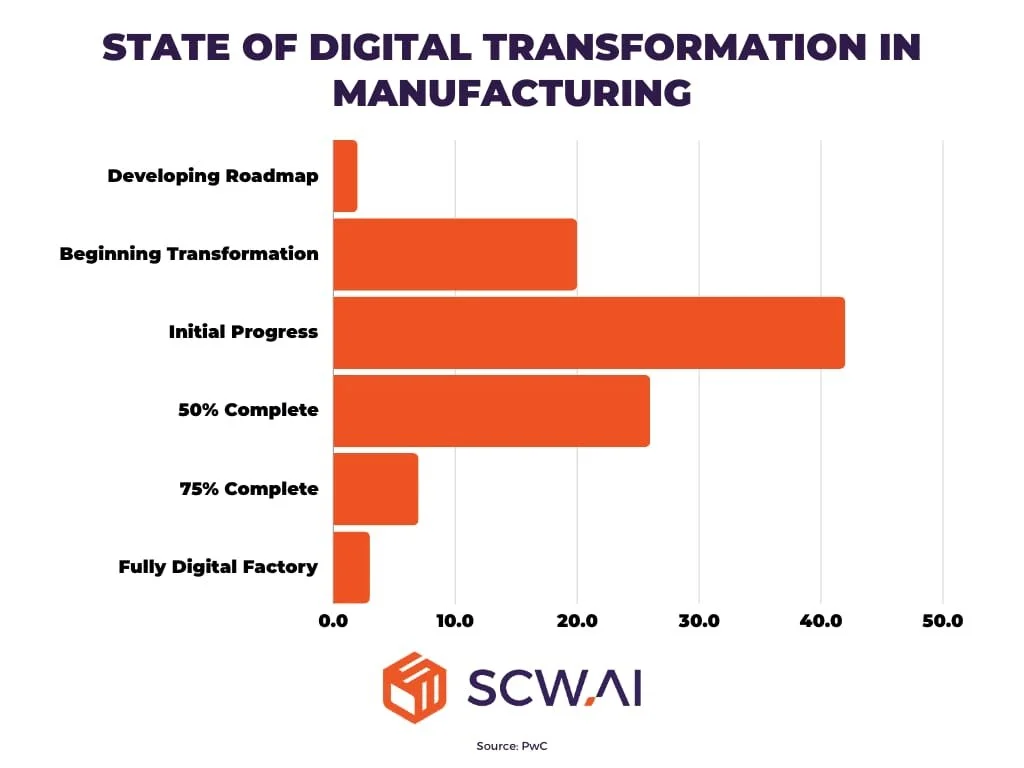
State of digital transformation in manufacturing, indicating progress levels
The benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing are well-documented and substantial. Modern PPAP implementations deliver increased efficiency, quality improvement, improved customer experience, reduced costs, and enhanced digital culture. These benefits align perfectly with the core objectives of PPAP: ensuring consistent quality while optimising process efficiency.

Benefits of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
The KEVOS Advantage: Strategic PPAP Implementation
For engineering design and drafting service providers like KEVOS, understanding and implementing PPAP represents more than just compliance—it’s a strategic differentiator that opens doors to new markets and strengthens client relationships. The key lies in recognising which PPAP elements offer the greatest opportunity for value creation.
Design Records represent perhaps the most critical element for engineering firms. These comprehensive drawings and specifications form the foundation of the entire PPAP process. When KEVOS provides accurate, detailed drawings with clearly marked special characteristics and comprehensive dimensional information, it directly supports multiple downstream PPAP elements. This foundational work reduces the risk of nonconformance and accelerates the approval process.
Engineering Change Management constitutes another area of critical importance. In today’s dynamic manufacturing environment, design changes are inevitable. KEVOS’s expertise in documenting and communicating these changes through clear Engineering Change Notices ensures traceability and maintains approval status throughout the product lifecycle.

Technical drawing with cross-sectional, front, and isometric views, including dimensions and annotations
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
The path to successful PPAP implementation is not without obstacles. Common challenges include insufficient technology infrastructure, demanding time and resource requirements, and capability gaps within organisations. Many companies struggle with too many documents and insufficient document control, making it difficult to standardise procedures across global supply chains.
However, these challenges are not insurmountable. Best practices for PPAP implementation include establishing clear and concise requirements, creating comprehensive PPAP packages, utilising specialised software solutions, training employees on procedures, and maintaining effective customer communication. The key is approaching implementation systematically, with adequate planning and resource allocation.
Seven Strategies For Successful Project Collaboration
The Future of PPAP: Industry 4.0 and Beyond
The future of PPAP lies in the convergence of traditional quality management principles with cutting-edge digital technologies. Industry 4.0 initiatives—encompassing modernisation, optimisation, and transformation—are reshaping how manufacturers approach quality assurance. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics are being integrated into PPAP processes to deliver unprecedented levels of efficiency and accuracy.
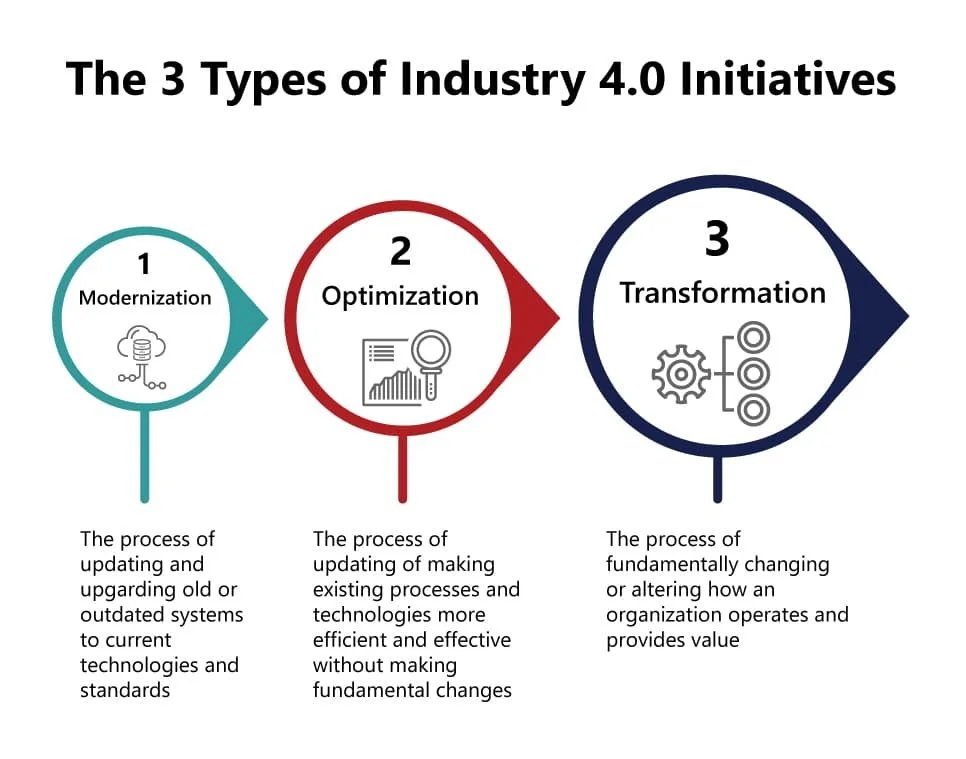
The 3 Types of Industry 4.0 Initiatives Include Modernisation, Optimisation, and Transformation
This technological evolution doesn’t diminish the importance of fundamental PPAP principles; rather, it amplifies their impact. Digital tools enable more sophisticated analysis, faster processing, and greater accuracy, but the underlying need for systematic quality validation remains constant.
A Roadmap for Success: Implementing PPAP Excellence
For engineering firms ready to embrace PPAP as a strategic advantage, success requires a structured approach.
PPAP Implementation Roadmap for Engineering Firms
Phase 1: Foundation Building (Weeks 1-4)
Week 1-2: Assessment and Planning
- Conduct PPAP Readiness Assessment
- Evaluate current design documentation practices
- Assess team knowledge of PPAP requirements
- Review existing quality management systems
- Identify gaps in processes and capabilities
- Develop Implementation Strategy
- Define PPAP objectives and success metrics
- Allocate resources and assign responsibilities
- Create project timeline and milestones
- Establish budget for training and tools
Week 3-4: Team Preparation
- PPAP Training Program
- AIAG PPAP manual review sessions
- Industry-specific requirements training
- Software tools familiarisation
- Best practices workshops
- Process Documentation
- Map current design workflow
- Identify PPAP integration points
- Create standardised templates
- Establish quality checkpoints
Phase 2: System Integration (Weeks 5-8)
Week 5-6: Technology Setup
- Digital Infrastructure
- Implement PPAP management software
- Set up document control systems
- Configure automated workflows
- Integrate with existing CAD systems
- Quality Management Integration
- Link PPAP requirements to design processes
- Establish measurement systems
- Create reporting dashboards
- Set up customer collaboration portals
Week 7-8: Process Standardisation
- Design Documentation Standards
- Update drawing templates for PPAP compliance
- Standardise special characteristics marking
- Implement change control procedures
- Create design review checklists
- Communication Protocols
- Establish customer interaction procedures
- Create submission tracking systems
- Develop escalation processes
- Set up regular review meetings
Phase 3: Pilot Implementation (Weeks 9-12)
Week 9-10: Pilot Project Selection
- Project Criteria
- Select low-risk, representative projects
The implementation journey typically spans 16 weeks, progressing through four distinct phases: Foundation Building, System Integration, Pilot Implementation, and Full Deployment.
The Foundation Building phase focuses on assessment and preparation, ensuring that the organisation has the necessary knowledge, processes, and infrastructure to support PPAP implementation. This includes conducting readiness assessments, developing implementation strategies, and establishing comprehensive training programs.
System Integration involves implementing the technological infrastructure necessary for modern PPAP management. This includes digital document control systems, automated workflows, and integration with existing CAD systems. The goal is creating a seamless environment where PPAP requirements are naturally embedded in existing design processes.
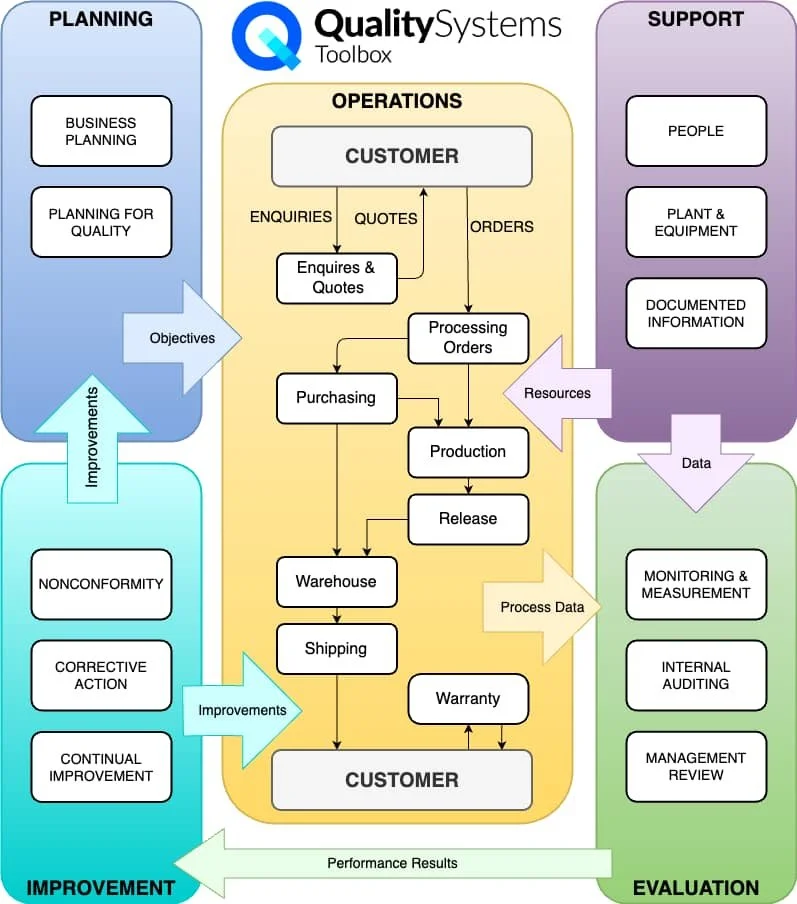
Process Map Showing Interplay Between Business Functions In A Quality Management System
The Continuous Improvement Imperative
PPAP implementation is not a destination but a journey of continuous improvement. The most successful organisations treat PPAP as part of a broader quality management system that encompasses planning, operations, support, evaluation, and improvement. This holistic approach ensures that quality remains a central focus throughout the entire product lifecycle.
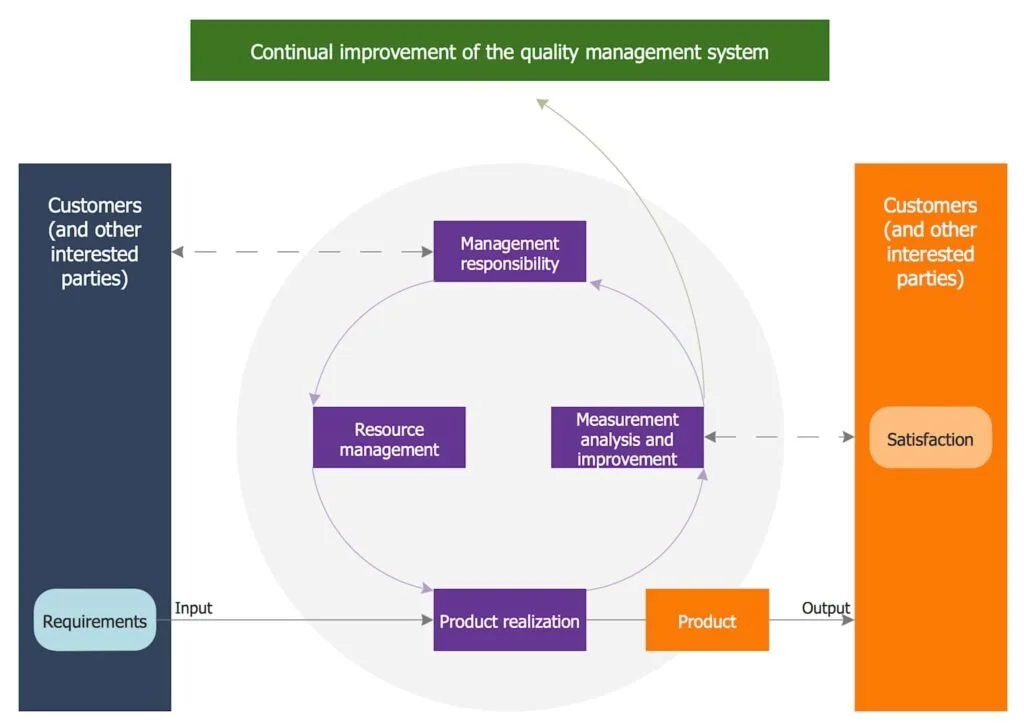
Process Flowchart Illustrating a Quality Management System
The integration of PPAP with Six Sigma methodologies and other quality management frameworks creates powerful synergies. Statistical Process Control, Measurement System Analysis, and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis all contribute to the robustness of the PPAP process. When these tools work in concert, they create a comprehensive quality ecosystem that dramatically reduces the risk of defects and nonconformance.
Success Stories: PPAP in Action
The real-world impact of PPAP implementation can be seen across numerous industry success stories. Tier 1 automotive suppliers have leveraged PPAP expertise to manage thousands of suppliers globally, achieving on-time deliveries and maintaining relationships with major OEMs like Tesla, Ford, and GM. These successes demonstrate that PPAP is not merely a compliance requirement but a strategic capability that drives business growth.
In the aerospace industry, fastener manufacturers have used PPAP to validate complex supply chains and ensure compliance with stringent quality requirements. The systematic approach of PPAP provides the documentation and verification necessary to meet the demanding standards of aerospace applications.

A list of additional manufacturing services, including PPAP
The Collaborative Foundation
At its core, PPAP success depends on effective collaboration between suppliers, customers, and engineering service providers. The process requires clear communication, shared understanding of requirements, and commitment to continuous improvement. For engineering firms like KEVOS, this collaborative approach creates opportunities to add value beyond traditional design services.
The evolution of PPAP from its automotive origins to widespread adoption across industries demonstrates the universal applicability of its principles. Whether in aerospace, electronics, medical devices, or other precision manufacturing sectors, the fundamental need for systematic quality validation remains constant.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators
The success of PPAP implementation must be measured across multiple dimensions. Quality metrics include submission approval rates (targeting >95% first-time approval), customer satisfaction scores (>90%), defect reduction (50% improvement), and compliance rates (100% PPAP compliance). These metrics provide objective measures of PPAP effectiveness.
Efficiency metrics focus on time and resource optimisation. Successful implementations typically achieve 60% reduction in PPAP preparation time, 40% improvement in resource utilisation, 50% decrease in preparation costs, and 25% improvement in overall project delivery. These improvements directly impact profitability and competitive positioning.
Business impact metrics capture the broader strategic value of PPAP capabilities. Organisations typically see a 30% increase in PPAP-related business, expanded market share in regulated industries, >95% customer retention rates, and enhanced competitive differentiation.
The Global Perspective: PPAP’s Worldwide Impact
The influence of PPAP extends far beyond its American automotive origins. The process has been adapted and adopted globally, with variations like the German VDA’s Production Process and Product Approval (PPA/PPF) serving similar functions in European markets. This global standardisation has facilitated international trade and collaboration, creating a common language for quality assurance across borders.
The digitalisation of both PPAP and PPA/PPF processes has further accelerated global adoption. Cloud-based systems enable real-time collaboration between suppliers and customers regardless of geographic location. This technological enablement has made it possible for engineering firms to serve global markets more effectively.
Conclusion: The Strategic Imperative
Understanding PPAP is indeed the key to quality in engineering production, but it represents something far more significant than a compliance requirement. PPAP embodies a fundamental shift in how organisations approach quality—from reactive inspection to proactive prevention, from isolated processes to integrated systems, from manual documentation to digital transformation.
For engineering design and drafting firms like KEVOS, mastering PPAP opens doors to new markets, strengthens client relationships, and creates sustainable competitive advantages. The firms that embrace PPAP as a strategic capability—rather than viewing it as a burden—will find themselves well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly quality-conscious global marketplace.
The journey from chaos to excellence is not always smooth, but the destination is worth the effort. As manufacturing continues to evolve toward Industry 4.0 and beyond, the principles embodied in PPAP—systematic validation, continuous improvement, and collaborative excellence—will remain constant. Organisations that understand and implement these principles today will be the quality leaders of tomorrow.
The story of PPAP is ultimately a story of transformation—of industries, organisations, and individuals committed to the pursuit of excellence. In a world where quality is not just desired but demanded, understanding PPAP is not just beneficial—it’s essential. The question is not whether to implement PPAP, but how quickly and effectively it can be done. The future of quality engineering depends on the answer.
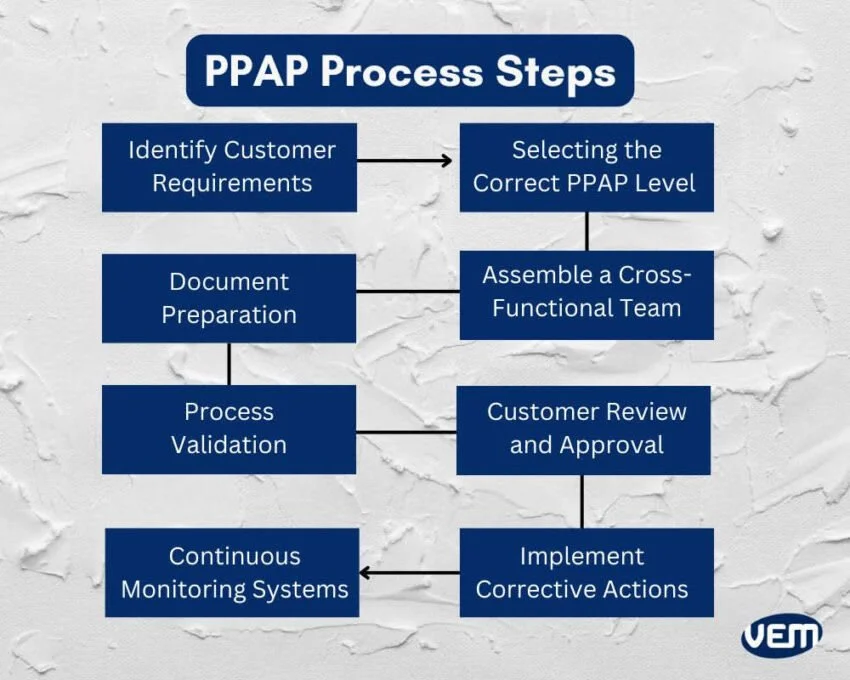
Flowchart illustrating the PPAP process steps
The path forward is clear: embrace PPAP as both a methodology and a mindset, leverage technology to amplify its benefits, and commit to the continuous improvement that lies at its heart. In doing so, engineering firms will not just meet today’s quality requirements—they will help define tomorrow’s standards of excellence.